The DMart business model is extremely successful even after being the cheapest retail store out there. How does Dmart make money if they’re able to offer prices that are lower than the MRP and even most of its competitors? Let’s dive right into it now!
How does DMart make money?
DMart makes money by optimizing operations for low cost and high volume sales. The company displays products that are consumed the most and strikes deals with suppliers to get the lowest possible prices on all products. This makes DMart a highly profitable, high-volume convenience store.
DMart’s retail store business is considered one of the most successful supermarket chain models because of a very unique business strategy that they’ve followed over the years. Their brand speaks just this one thing: “Everyday low cost/Everyday low price” (EDLC/EDLP).
Let’s answer some quick questions about D Mart before we dive into the business.
What is D-Mart?

Dmart is an Indian retail supermarket/hypermarket that sells everything from groceries to clothing at an extremely low cost. The retail chain thrives on being able to offer the cheapest prices for its customers.
What is the full form of D-Mart? The brand is named after its founder, Ramkrishna Damani. The “D” stands for “Damani”. What started as a single retail shop, has now become one of the largest retail chains in India.
Who is the owner of D Mart? Dmart is owned by Avenue Supermarket (NSE: DMART), a public company with a market valuation of over INR 155,000 crore (INR 1.5 Trillion).
Who is the CEO of D Mart? Ignatius Navil Noronha is the CEO of DMart Stores with 1.34 crore (13.4 million) shares of Avenue Supermarkets that are worth INR 3,100 crore (USD 408 million) as of this writing.
Decoding the DMart Business Model
D Mart gained the attention of its customers when it established its brand as a low-cost essentials retailer. If you look at the products that make it to the shelves of D Mart, you’ll notice that most of the products are things that are extremely necessary for the Indian consumer’s day-to-day activities. Along with the DMart store, they also started out with DMart ready an online shopping experience for customers who love DMart prices.
Basic costs involved for any retail store
To understand why Dmart is able to offer low prices, let’s understand the basic costs for an organized retail store or supermarket.
Here are the 4 major costs that eat up in any retail store or supermarket’s profit:
- Cost of location – This includes the monthly fixed payments that need to be paid for a leased or owned land with an ongoing loan if any
- Cost of inventory – The next cost that’s involved is the inventory. Depending on the size and style of store, the inventory costs may vary
- Cost of employees – The salaries, bonuses, and other rewards paid out to employees on a monthly and yearly basis
- Maintenance Costs – The final major cost is for maintenance which includes electricity, cleaning, repairs and replacements of in-store technology, furniture, etc.
When a retailer understands the tricks to run a lean business store, the result is an increase in profits for the business. Here’s where D-Mart takes the spotlight! They’ve mastered the art of running lean and pass on the profit to the customers as discounts. Let’s understand how they do it.
What’s the Secret Behind DMart’s Success?

A ton of factors went into building DMart as a brand into what it is right now, and there’s a lot that other businesses can learn from it. DMart mastered the art of cost reduction while satisfying their customers to the fullest. Here’s how:
- 85-90% of D Mart stores are on owned land reducing monthly rental cost: The highest cost for other retailers is the monthly lease or rental costs. D-Mart is able to save that since they own most of the land that the stores are run on.
- All products purchased from the source to ensure the best prices: Dmart makes sure they get the best price possible for a product. And that’s possible by cutting out the middle-men.
- On-time payments to suppliers increase negotiating power: Major retail stores pay the suppliers after 60 days of the product delivery. D-Mart pays the suppliers within 10 days. This provides higher negotiation power to the brand.
- Employees trained and upskilled: With regular training and upskilling, the employees are able to perform more tasks that would otherwise require adding new employees. This saves the overall cost of hiring and keeps employees engaged with the company.
- Contract labor: A major chunk of D Mart’s employees is contract-based. They’re paid on an hourly or weekly basis for the amount of work done. Contractual employees trained to perform multiple tasks reduce the number of employees required to make certain of the smooth running of the store operations.
- Taking steps towards green buildings: In the year 2018-19, D-Mart took steps towards running on green power. They have installed solar rooftops on multiple stores and are continuing to do the same with more stores as the months go by. See the image above for reference.
- Stocking limited products: D-Mart uses data to understand what products are purchased the most and only stock those products in bulk. Anything else is stocked in a limited quantity. That’s why D Mart stores inventory runs out fast and the suppliers are able to keep consistent cash flow for themselves with refilling.
- Efficient Supply Chain: The business runs profitably because of the efficiency that Ramkrishna Damani has achieved because of his relations with vendors and suppliers since the initial stages. They restock the inventory timely and get paid before the due date.
How does DMart make money?
With such lean operations, DMart has the potential to make a lot of profit due to the enormous volumes of people who purchase essentials. In the 18 years of their existence, DMart hasn’t had a store shut down due to a lack of profits.
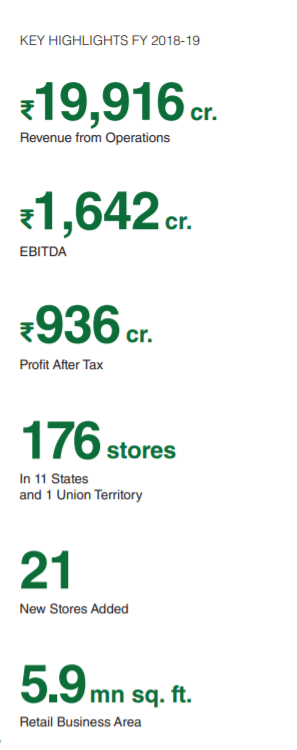
Even after offering ever-increasing discounts, endless buy-one-get-one-free offers, and perfect availability of products, D-Mart earns INR 936 Crore (9.3 Billion) net profit in the year 2019! With over 18 years of experience in the consumer retail market, the brand has a nationwide store count of 176.
That’s less than 10 store additions per year. Comparatively, Reliance retail was founded in 2006 and has 10,000 stores nationwide. The expansion rate is 714 stores per year!
But on the other hand, D Mart has never made a loss in any of their stores. Credits to Mr. Damani’s relationship-building skills which have kept him in profit even after years of offering highly discounted products.
Here’s an additional fact: In 2019, they made a profit of INR 1500 per sq. ft. Their current revenue per square feet is at INR 35,647 with a revenue growth rate of 9% YoY.
Let’s move to find out why Mr. Damani follows this value retail approach.
DMart’s Marketing Strategy
The strategy is its discounts and its customers. DMart thrives on word-of-mouth marketing. With the homemakers being raving fans of DMart, they have never had to spend money on marketing to customers.
The Indian audience does not shy away from a good bargain, even if that means additional travel. Damani understands this and caters to this exact mindset. Since Indians are generally talkative with neighbors and friends, the marketing doesn’t take long.
Why has D-Mart continued to stay profitable?
Mr. Damani is a value investor and believes in moving slow. His approach to the DMart business model has been that of value retailing. With a slow approach where the business only expands when it starts turning a profit, the store addition and expansion will be slower. But the long term survivability of the business increases by a greater proportion.
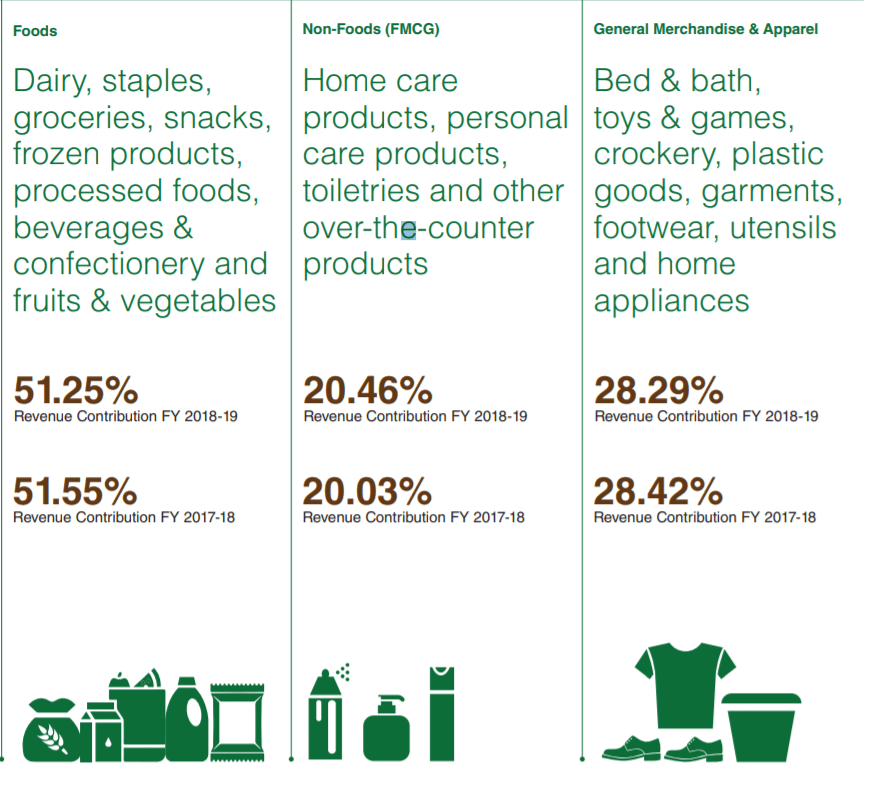
As you can see, 51% of their revenue is generated from the staple items and 28% from their clothing venture. Without losing their focus, as they continue to serve highly discounted food items and other staples, the DMart business model will continue to thrive in this market of needs.
Who are D-Mart’s Competitors?
There are lots of retail chains worldwide, and many of them have ventured into the India markets, along with the existing Indian supermarket chains. Here’s a list of competitors for DMart:
- Future Retail/Big Bazaar
- Reliance Retail
- Walmart
- Aditya Birla’s More Megastore
- HyperCITY
- etc..
Their largest competitor at present is Big Bazaar with the same focus and similar style of running their stores. Apart from retail, DMart has also ventured into basic clothing. Their competitor in the clothing space is Aditya Birla Fashion which was one of the initial retail stores that offered good quality clothing at very low prices.
What are the long term prospects for DMart?
With shoppers moving online, the only reason why they still visit the DMart store was for discounts. DMart ready is their online shopping platform that lets users buy products at the discounted prices.
In the long term, the drop in footfalls at the stores will result in better profitability as the number of stores can be reduced and the focus moved online only.
Also, as the costs for energy efficient systems within the stores gets paid off, the stores will operate on negligible electricity costs.
Ending words…
The DMart business model is extremely interesting albeit an old-school one. Major retailers and even startups would probably not look into DMart for inspiration, but in my opinion, that’s how a business should be looked at. You don’t need to serve your products at the cheapest possible cost but running lean can make your business survive even the harshest market situations. If you’re interested in more business models, have a look at how does Duolingo make money.


![Read more about the article How does BeReal make money? [Updated]](https://moneymodels.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/How-does-BeReal-make-money-300x150.png)
![Read more about the article How Does Whatsapp Make Money? [Revenue Model]](https://moneymodels.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/How-does-WhatsApp-make-money-300x150.jpg)
![Read more about the article How does Humble Bundle make money? [Business Model]](https://moneymodels.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/How-does-Humble-Bundle-make-money-1-300x150.png)