A long time ago, businesses and large organizations required huge investments to host their own servers and websites. But with the rise of the Infrastructure as a Service – IaaS business model, a lot has changed.
Now, anyone with a few dollars can go online with a full-fledged website or web app! And that has given rise to this mammoth as an industry of its own.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a form of cloud computing where users can rent hardware resources on a per-use or per-month basis.
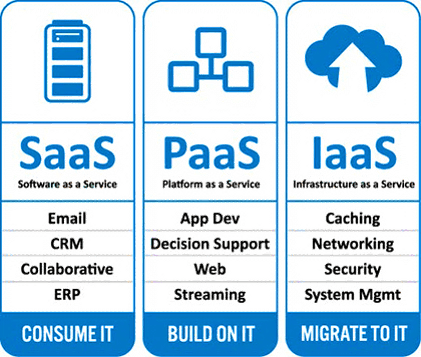
Users access the hardware through a web interface or using an SSH connection.
Think of IaaS as renting a hardware server in a different city. You can access the resources from a remote connection but you don’t have to manage the uptime, pay for the electricity, or handle the maintenance of the server.
What is the IaaS Business Model?
The Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) business model is a method of renting servers and computing power, without the added maintenance and management that accompany when you host physical servers on-premise.
In simple words:
Suppose you want to host a website. Instead of setting up a server and managing it yourself, you pay someone who already has a server to allocate space for your website. They set everything up, and give you access to your website.
You’re happy because the website is online. And the person you paid for the server is happy because they can recoup some of the maintenance costs. As the person gets more clients, they can manage the server at a healthy profit too. This essentially is the IaaS business model.
I’d go as far as to say this:
The IaaS business model is a solution to all the server management and maintenance problems that system administrators have faced for years.
Because the Infrastructure as a Service solves such a big problem for IT companies, it has gained huge popularity.
Currently, the IaaS market is valued at over $50 billion and is estimated to grow at 26.9% YoY.
How does the IaaS Business Model work?
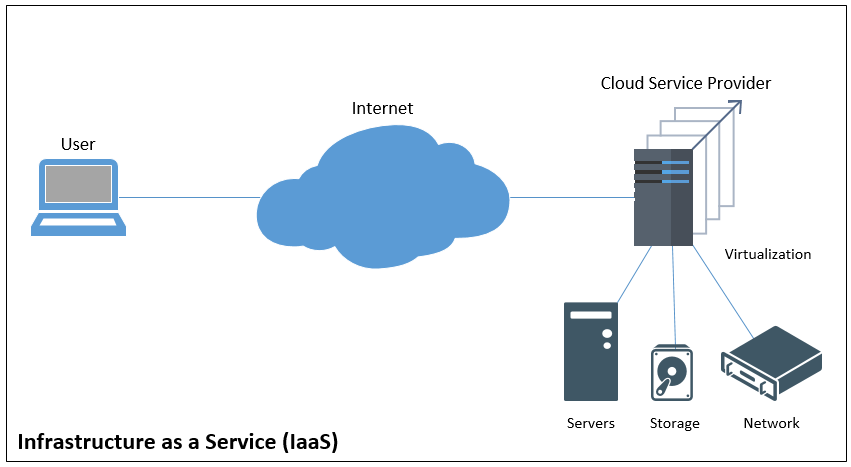
When you rent a server from an IaaS service provider, you outsource the following activities:
- Uptime management
- Storage device maintenance and management
- Hardware and software upgrades
- Software and data security
- Electricity costs
- Hardware depreciation
You’re essentially saving time and costs for yourself and your company as system administrators can spend more time on what’s important to improve company infrastructure.
Because this is a win-win situation offering cheaper costs to both, large IT companies and small businessmen venturing into the business world, the IaaS business is widely used. In fact, if the growth continues at a conservative estimate of 23% – by 2027, the IaaS industry could reach $201.83 billion in valuation.
How does an IaaS business make money?
IaaS businesses make money by renting out their equipment. After paying for the server maintenance and electricity costs, the remaining amount is the profit.
As an IaaS business continues to scale and use virtualization to serve even more users per server, the cost of maintenance lowers further.
While the initial investments for an Infrastructure as a Service business owner are high, any IaaS business can turn profitable in the long term as the cost is much lower with the use of virtualization technologies like Docker and Droplet systems.
In 2021, IaaS businesses are estimated to make over $63.8 billion with a 20% share in the combined SaaS and PaaS markets. We estimated this figure by calculating a 27% growth rate in the IaaS industry as per Statista.
Infrastructure As A Service in Real Life
Let me explain how IaaS works with a real life example (a personal one).
Recently, our team had to build a web-app for a client. And we had two choices.
- Use their existing on-premise server
- Rent a Google Cloud compute instance
Since their in-house servers were slow and dated, we decided to move ahead with the Google Cloud Compute service.
The estimated costs for renting a basic virtual server were $100 a month, accounting for the occasional spikes in app usage.
Additionally, the setup time was just 2 hours!
Compare that with their in-house server, the costs would be anywhere from $500 and above considering a system administrator was dedicated for the maintenance and management.
Apart from that, we’d also need to spend a lot more time setting up the server to be fast, serve web requests on time, and be optimized and available for all the traffic 24×7. That sure would have been a lot more management.
So, here’s how we setup the entire server on Google cloud:
- Activate the billing account for Google cloud
- Enable a compute instance with Ubuntu server
- Allowed the instance to complete the setup process
- Once the instance was setup, I SSH’d into the server and sent across the app code.
- Downloaded the compilers and required packages to run the app
- Compiled the code
- And we were all set
This is the power of the IaaS business model! Had I used a more common programming language to build the app, I’d have even less setup to go through.
Conclusion
That’s all for the IaaS businesses here. You can read how how Google makes money here.


![Read more about the article How does ETrade Make Money? [Business Model]](https://moneymodels.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/How-does-eTrade-make-money-300x150.jpg)

![Read more about the article How Does LinkedIn Make Money? [Business Model]](https://moneymodels.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/How-does-Linkedin-make-money-300x150.jpg)